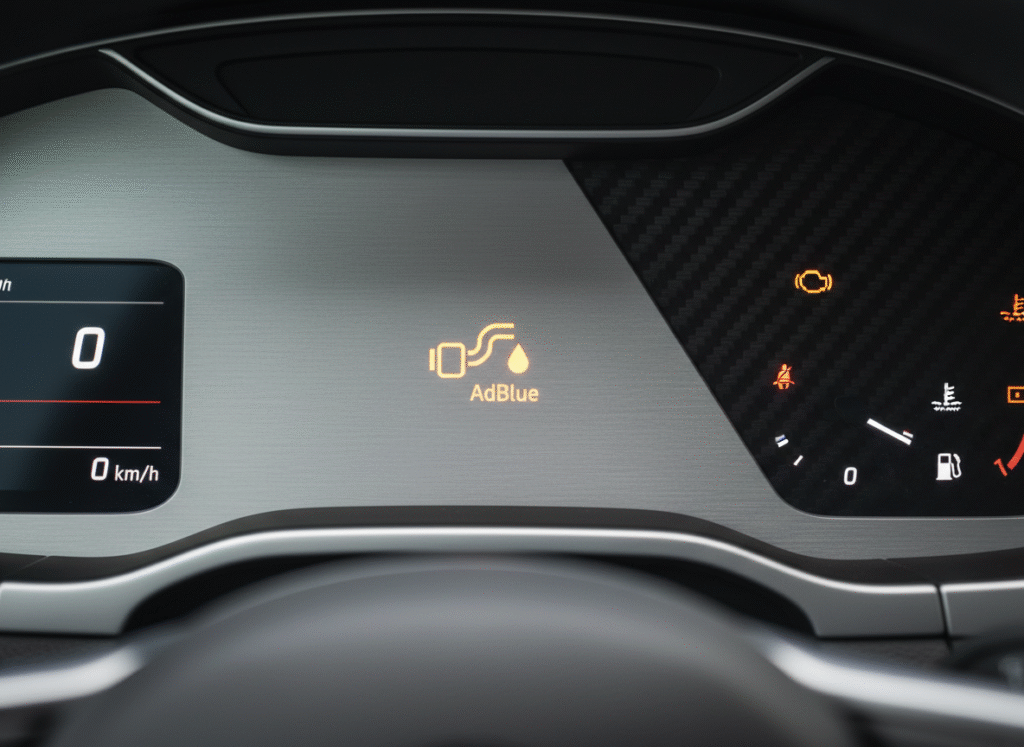
What Does AdBlue Do is a critical component in modern diesel engine technology, specifically designed to reduce harmful emissions and ensure compliance with stringent environmental regulations. This comprehensive guide will explore what AdBlue is, how it works, and its impact on both vehicle performance and the environment.
1. Introduction to AdBlue
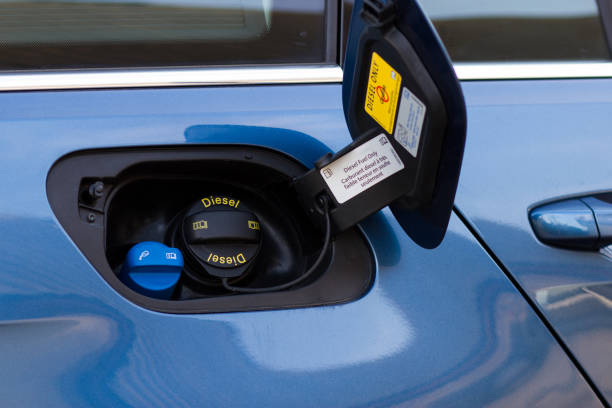

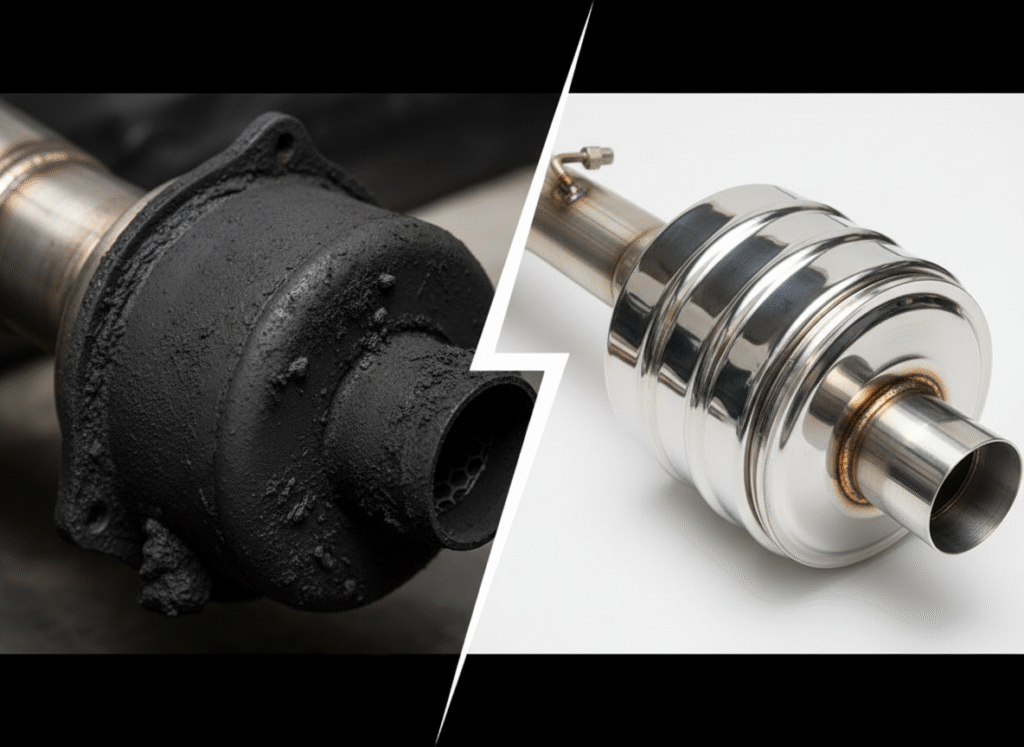
AdBlue is a trademarked name for a solution that is used in Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from diesel engines. It’s a clear, non-toxic fluid that consists of 32.5% urea and 67.5% deionized water. The solution is injected into the exhaust stream, where it helps to convert NOx gases into harmless nitrogen and water vapor.
2. The Environmental Challenge
Diesel engines, while offering impressive fuel efficiency and power, have traditionally been associated with higher NOx emissions compared to gasoline engines. NOx gases are pollutants that contribute to smog, acid rain, and respiratory problems. As environmental regulations have tightened globally, there has been a pressing need for technologies that can reduce these emissions. AdBlue is one of the key solutions developed to meet these new standards.
3. The Science Behind AdBlue
3.1 What is Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)?
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) is a technology that uses AdBlue to neutralize NOx emissions. In an SCR system, AdBlue is injected into the exhaust gases before they enter a catalyst. The catalyst then facilitates a chemical reaction that converts NOx into nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O), which are much less harmful.
3.2 The Chemical Reaction
The core chemical reaction involved in SCR with AdBlue is:
2NO+2H2O+AdBlue→N2+4H2O2 \text{NO} + 2 \text{H}_2\text{O} + \text{AdBlue} \rightarrow \text{N}_2 + 4 \text{H}_2\text{O}2NO+2H2O+AdBlue→N2+4H2O
In simpler terms, the urea in AdBlue breaks down into ammonia (NH3) in the hot exhaust gases, which then reacts with NOx to form nitrogen and water.
4. How AdBlue is Used
4.1 Storage and Handling
AdBlue is stored in a separate tank within the vehicle, separate from the diesel fuel tank. The system is designed to be easy to refill, and the fluid is generally available at service stations and auto parts stores. It’s important to handle AdBlue carefully, as contamination or incorrect handling can affect its performance.
4.2 Injection System
The AdBlue solution is delivered into the exhaust stream through an injector located upstream of the SCR catalyst. The amount of AdBlue injected is controlled by the vehicle’s engine management system, which ensures that the correct amount is used based on engine load and operating conditions.
5. Benefits of Using AdBlue
5.1 Reduced Emissions
The primary benefit of AdBlue is its ability to significantly reduce NOx emissions. This helps vehicles comply with stringent emissions regulations, such as Euro 6 standards in Europe and Tier 4 standards in North America.
5.2 Improved Air Quality
By reducing NOx emissions, AdBlue contributes to improved air quality. Lower NOx levels help to decrease the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, leading to cleaner air and better public health outcomes.
5.3 Enhanced Engine Performance
AdBlue doesn’t only help with emissions; it can also improve engine performance. By reducing the need for engine modifications to meet emissions standards, AdBlue allows engines to operate more efficiently and reliably.
6. AdBlue and Vehicle Maintenance
6.1 Monitoring and Refilling
Modern vehicles equipped with SCR systems typically have sensors that monitor AdBlue levels and alert the driver when it’s time to refill. Running out of AdBlue will usually not prevent the vehicle from starting, but it will lead to a gradual reduction in engine performance and, eventually, a shutdown if the fluid is not replenished.
6.2 System Maintenance
SCR systems are generally low-maintenance, but it’s crucial to use the correct AdBlue quality and ensure that the system is free from contaminants. Regular vehicle servicing will include checks on the SCR system and AdBlue levels.
7. AdBlue in the Market
7.1 Availability and Cost
AdBlue is widely available and relatively inexpensive compared to other vehicle fluids. It’s sold in various quantities, from small containers for personal vehicles to bulk supplies for commercial fleets. The price can vary depending on the region and supplier, but it is generally affordable.
7.2 Quality Standards
Not all AdBlue is created equal. It’s important to use AdBlue that meets the ISO 22241 standard to ensure optimal performance and avoid damage to the SCR system. Genuine AdBlue is produced under strict quality controls to maintain the correct concentration and purity.
8. Challenges and Considerations
8.1 Temperature Sensitivity
AdBlue can be sensitive to extreme temperatures. In cold weather, it can freeze, which may affect its flow and effectiveness. However, most SCR systems are designed with heating elements to prevent freezing and ensure reliable operation.
8.2 Environmental Impact
While AdBlue helps reduce NOx emissions, it’s not without its environmental impact. The production and transportation of AdBlue involve energy and resources. However, the benefits of reduced air pollution generally outweigh these impacts.
9. Future Trends in Emission Reduction

9.1 Technological Advances
Research and development in emission reduction technologies are ongoing. Future advancements may include improved SCR systems, alternative fuels, and further enhancements to AdBlue solutions. The goal is to continue reducing emissions while improving vehicle efficiency.
9.2 Legislative Changes
As environmental regulations continue to evolve, vehicles will need to adapt to meet new standards. AdBlue and SCR technology will likely play a crucial role in meeting these future requirements.
Conclusion
AdBlue represents a significant advancement in reducing diesel engine emissions. By using AdBlue in conjunction with SCR technology, vehicles can significantly cut down on harmful NOx emissions, contributing to better air quality and compliance with environmental regulations. Understanding how AdBlue works, its benefits and its role in modern vehicles helps drivers and fleet operators make informed decisions about their emissions control strategies.
As environmental standards become more stringent and technology continues to evolve, AdBlue will remain a key player in the effort to create cleaner, more efficient diesel engines.